Thoracic Surgery Excellence
Reliable Quality of Thoracic Surgery
Professional lung cancer specialists and a high-quality medical team ensure the quality of thoracic surgery for patients.

Personalized Thoracic Surgery Plans
Thorough preoperative evaluation by an experienced thoracic surgeon to select the optimal thoracic surgery approach and minimize functional loss.
Advanced Thoracic Surgery Skills
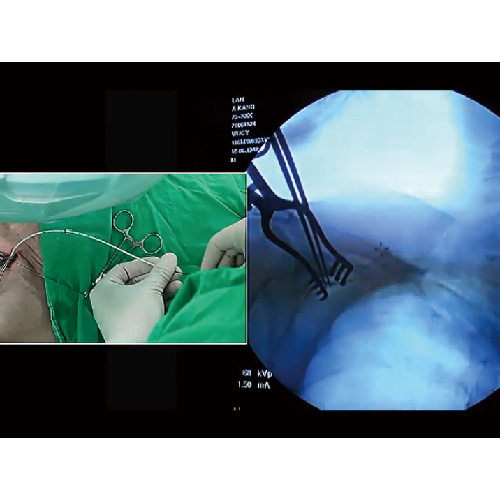
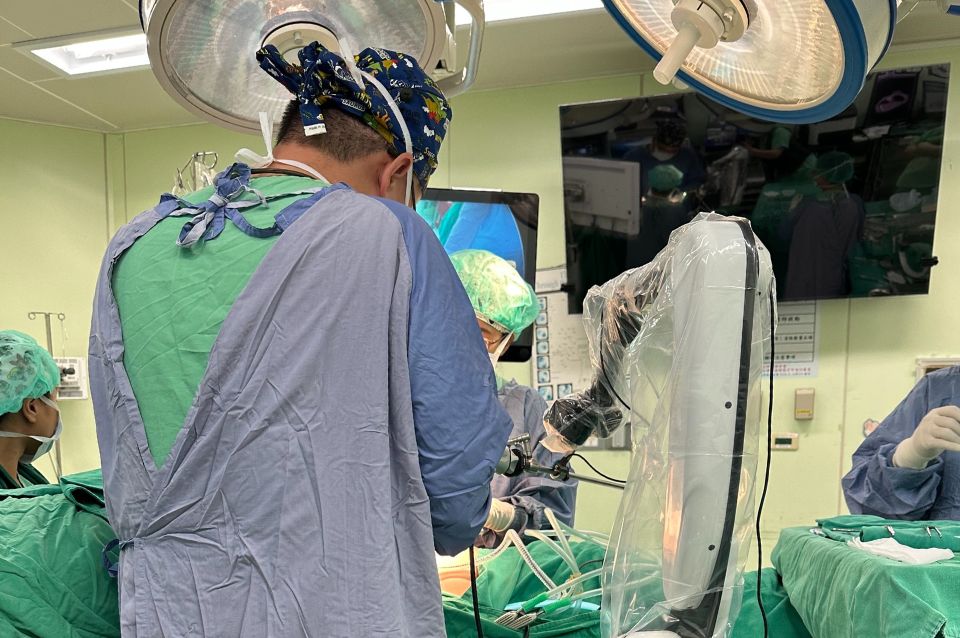
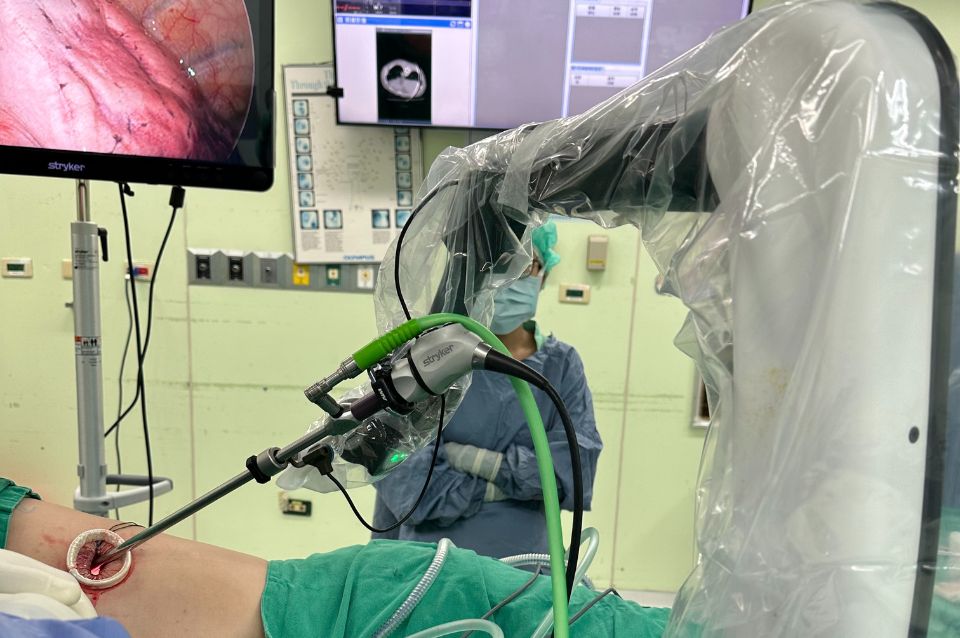
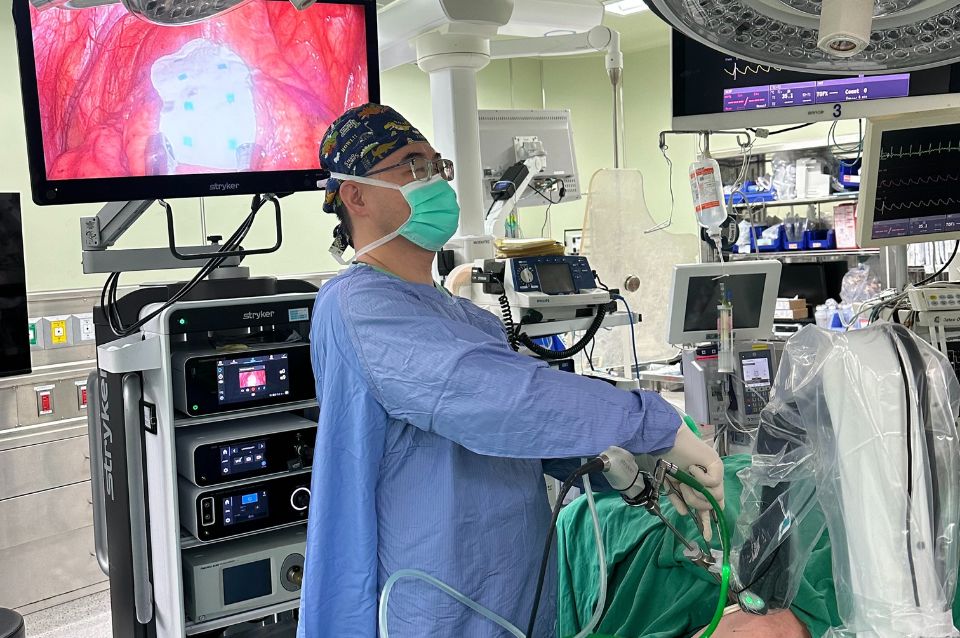
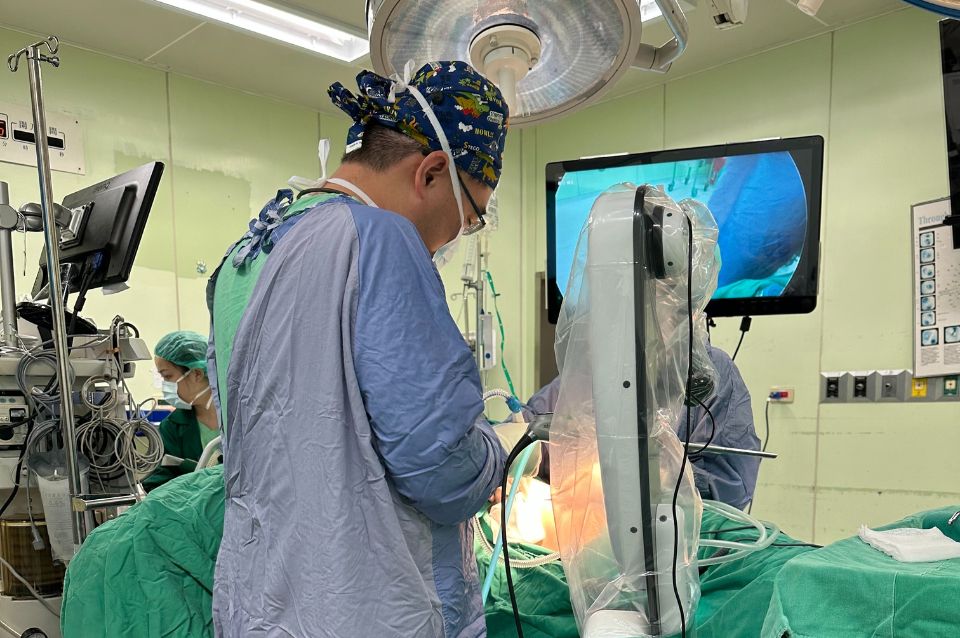
Proficient in advanced surgical techniques such as single-port thoracoscopic surgery and single-port robotic surgery.
Years of Clinical Research and Surgical Experience
Experienced in various thoracic conditions, such as lung cancer, mediastinal tumors, intravenous port, and lung ground-glass opacities.
Considering Patient Conditions to Minimize Surgical Damage
Comprehensive preoperative evaluation, taking into account the patient's physical condition, to reduce surgical risks and damage to a minimum.
Postoperative Care by Experienced Thoracic Surgeons
Thoracic surgeons track imaging to detect recurrence early and optimize thoracic surgery outcomes.
Thoracic Surgeon
DR. CHING-YANG WU
Lung surgery is complex and requires precise technique. Its success largely depends on the experience and skills of the thoracic surgeon.
- Single-port thoracoscopic surgery for lung cancer/lung tumors
- Single-port robotic surgery for lung cancer/lung tumors
- Single-port thoracoscopic surgery for mediastinal tumors
- Intravenous port implantation (Chemoport)
- Follow-up and treatment of lung ground-glass opacities
About DR. CHING-YANG WU
- Attending Thoracic Surgeon at Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital
- Associate Professor of Surgery at Chang Gung University
- Associate Professor of Surgery at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital
- Instructor of the Taiwan Society of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
- Instructor of the Taiwan Society of Thoracic Surgery

Thoracic SurgeonGet Immediate Help
Thoracic Booking
Chang GungTaoyuan
- Address:No. 123, Dinghu Rd., Guishan Dist., Taoyuan City
- Call to Book:03-3196200
- Clinic Hours:Thu. 8:30 AM – 12:00 PM
- Book Now:Taoyuan Chang Gung Thoracic Surgery
Chang GungLinkou
- Address:No. 5, Fuxing St., Guishan Dist., Taoyuan City
- Call to Book:03-3281200
- Clinic Hours:Fri. 1:00 PM – 5:00 PM
- Book Now:Linkou Chang Gung Thoracic Surgery
Types of
Thoracic
Surgery
SERVICE
Lung Cancer Surgery3D imaging
3D imaging aids tumor resection planning, with CT localization and...
MediastinumHolistic Evaluation
Considers tumor size, location, and involvement of vital organs, followed...
Port Placement SurgeryPort A
Considers the patient's treatment needs and vascular involvement of...
Lung GGOImaging Evaluation
Evaluate size, density changes, and initial imaging...
Timing for Thoracic Care
Thoracic symptoms are often non-specific, making diagnosis challenging.
Here’s a quick guide to common signs.
Lung Tumors
Small lung tumors often go unnoticed, as they typically do not cause symptoms unless they affect critical thoracic structures or spread to other parts of the body.
If a lung tumor compresses vital thoracic structures or spreads to other areas, symptoms may include shortness of breath, wheezing, or hemoptysis or cough with blood-stained sputum.
If these symptoms occur, seek prompt medical attention to confirm the tumor’s nature and plan treatment.
Esophageal Tumors
Symptoms depend on tumor compression, causing difficulty swallowing and weight loss as it worsens.
If these symptoms occur, further evaluation with chest CT, upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, or esophagography is recommended to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant and to plan appropriate treatment.
Esophageal Disorders
If you experience difficulty swallowing, a sensation of food being stuck, pain when swallowing, weight loss, or frequent regurgitation of undigested food, seek immediate evaluation at a thoracic surgery clinic.
Mediastinal Tumors
When mediastinal tumors cause compression or severe local invasion, symptoms like wheezing, limb swelling, drooping eyelids, coughing, or anemia may occur.
Consult a thoracic surgeon promptly for further evaluation.
Pneumothorax
Air leaks from the lungs, causing pressure buildup and lung collapse.
Symptoms include chest tightness, shortness of breath, low blood pressure, and palpitations (rapid heart beat).
It is common in tall, thin young men or patients with COPD. High-risk patients should seek evaluation promptly.
Empyema
Empyema is pus in the chest cavity, often due to untreated lung infections.
Symptoms include fever, chest tightness, and pain. Seek medical attention if symptoms follow a recent respiratory infection.
Lung Abscess
A lung abscess is caused by infection leading to tissue necrosis and pus buildup.
Symptoms include productive cough, blood-stained sputum or hemoptysis, and fever. If it ruptures into the pleural cavity causing empyema, chest tightness and pain may occur.
Seek medical evaluation for diagnosis and treatment.
Pleural and Pericardial Effusion
Pleural effusion compresses the lungs, causing collapse and shortness of breath.
Pericardial effusion can obstruct blood flow, causing shortness of breath, low blood pressure, and rapid heart rate. Seek medical attention if symptoms occur.
Thoracic Surgery Process
-
 1
1Disease Evaluation
Assess disease severity with imaging tests.
-
 2
2Preoperative Assessment
Confirm tumor location and plan surgery.
-
 3
3Thoracic Surgery
Perform surgery with minimal tissue damage.
-
 4
4Post-Surgical Care
Monitor recovery and pathology results.
-
 5
5Follow-up Care
Plan and compare follow-up care based on imaging.

Thoracic Surgery Q&A
Thoracic surgery covers conditions involving the lungs, trachea, esophagus, pleural cavity, mediastinum, and chest wall.
What should you know about it?
What is the definition of thoracic surgery?
Thoracic surgery involves operations on chest organs like the lungs, trachea, and esophagus.
It is used to treat lung cancer, mediastinal tumors, and other serious chest conditions.
What are the surgical options for lung cancer?
Most are performed via single-port thoracoscopy, with robotic assistance for precision.
Surgeons can also perform these procedures using robotic arms through a single incision.
How is lung cancer treated?
Treatment depends on tumor staging.
For tumors limited to one lung lobe or nearby lymph nodes, surgery with preoperative therapy is recommended.
If the tumor has spread beyond the same side of the chest, systemic treatments like targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy are used.
How long is the recovery after thoracic surgery?
Recovery after thoracic surgery varies by procedure and health condition.
Minimally invasive surgeries like single-port thoracoscopy allow discharge in 3–5 days and full recovery in 2–4 weeks.
Open surgery may take 6–8 weeks.
Good postoperative care helps ensure smooth recovery.
Lung tumor surgery risks? Any other options?
Surgery is the best option for malignant tumors with good heart and lung function.
If the tumor is benign or biopsy results are unclear, further biopsy or regular imaging follow-up for 2-3 years may be considered.
Is a ground-glass opacity always malignant?
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a neutral term, indicating tissue density higher than surrounding lung tissue.
It does not necessarily mean malignancy. "Ground-glass" refers to the foggy appearance on CT, caused by varying radiation penetration in GGO and normal lung tissue.
What are the symptoms of mediastinal tumors?
Mediastinal tumors may cause symptoms such as cough, chest fullness, shortness of breath, substernal pain, and weight loss.
However, some patients may remain asymptomatic, and tumors are discovered incidentally during imaging for other reasons.
What is an intravenous port?
An intravenous port provides easy vascular access for repeated treatments, reducing puncture frequency and improving comfort, especially for chemotherapy patients.
It is placed in the superior vena cava to minimize clot risk.
What are intravenous ports and their limits?
Intravenous ports included power-injectable ports( high injection pressure, up to 300 psi)and conventional one ( normal injection pressure, 180-200 psi).Power injectable port( high injection pressure ) support tumor treatment and contrast injection, while standard ones are for treatment only. Use non-traumatic needles and flush well after blood draws, transfusions, or IV nutrition to prevent infection or blockage.
Is intravenous port placement surgery safe?
The procedure is a safe outpatient surgery with minimal complications.
Dr. Wu's protocol reduces pneumothorax risks and the need for neck vein puncture. Mobile X-ray and ultrasound guidance ensure accurate placement and reduce infection and displacement risks.
Clinical vs. Pathological Staging
Clinical staging uses imaging, but may underestimate small or low-metabolism tumors.
Pathological staging is based on tissue examination, offering a more accurate assessment.
Around 10% of patients may receive a different treatment plan due to more severe pathological findings.
PressCoverage
 Health LTN
Health LTN
Advancing Large-Cell Lung Cancer Treatment: NCYU & Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou Collaborate
Associate Professor of NCYU and Dr. Wu’s team collaborate on large-cell lung cancer research, yielding significant findings...

Dr. Wu Receives AATS Graham Award at ASCVTS 2016
Dr. Wu excelled in the AATS Graham Award evaluation, delivering his research within the 12-minute limit (10-minute presentation + 2-minute Q&A)...

Dr. Wu’s Team Publishes Study on Three CT-Guided Techniques for Lung Lesion Localization in the European Journal of Radiology!
From September 2019 to August 2021, the team analyzed 418 patients with lung lesions, comparing three CT-guided...

Dr. Wu’s Team Publishes Study on 3D Simulation Training for Oncology Nurses in Seminars in Oncology Nursing!
Since implantable venous catheters are not visible to the naked eye and can only be identified by touch, improper handling may occur...

Dr. Wu’s Research on Implantable Venous Ports Published in Medicine!
Based on literature and clinical experience, Dr. Wu formulated a standard algorithm to evaluate the best entry vessel for...

Dr. Wu’s Lung Cancer Research Published in Medicine!
Many patients still experience recurrent non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). To investigate, Dr. Wu and his team reviewed data from 356 stage I lung cancer patients (2005–2011), finding...

Dr. Wu’s Team Publishes Prognostic Study on Lung Adenocarcinomas ≤2cm in the Journal of the Formosan Medical Association!
The study aims to identify unique prognostic factors with clinical significance. Retrospective analysis of cases from...

Dr. Wu’s Team Publishes Study on Postoperative Circulating Tumor Cells as a Predictor of Lung Cancer Recurrence in Diagnostics!
With extensive experience in lung cancer surgery, Dr. Wu’s team investigated whether changes in circulating tumor cells (CTC)...

Dr. Wu’s Study on Central Venous Catheter Tip Placement Published in Medicine!
After analyzing 346 cases, Dr. Wu found that 221 cases (63.9%) were in the non-migration group, 67 cases (19.4%)...

Dr. Wu’s Research on a New Implantable Injection Port Published in Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials!
With in-depth studies and extensive clinical experience in implantable intravenous ports, Dr. Wu has explored complications...

Dr. Wu’s Expertise
- 2011 Taiwan Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery New Scholar Award
- 2012 Taiwan Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery President’s Award
- 2014 Taiwan Vascular Surgery Smart Award
- 2015 Taiwan Vascular Surgery Smart Award
- 2016 AATS Graham Award
- 2020 Taiwan Thoracic & Critical Care Medicine Best Paper
- 2021 Taiwan Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery President’s Award
- 2023 Global Injection Port Consensus Conference
InfoVideo
What Is a Port-A?
Port-A types can be classified by catheter material, high-pressure compatibility, and injection port material. Catheters are mainly made of silicone…

Why Get a Port-A?
A brief overview of the reasons for Port-A placement…

What Is a High-Pressure Port-A?
An overview of high-pressure Port-A and its clinical benefits…

How Do Healthcare Providers Use a High-Pressure Port-A?
Identification and injection procedure for high-pressure Port-A…

Post-Op Care for Port-A
Daily activities remain unrestricted, but certain movements depend on port placement…

Port-A Placement: What to Expect
An implantable venous port, commonly known as a Port-A, serves as a reliable IV access for clinical treatments. It functions like an invisible socket placed under the skin, allowing injection needles—like…